Lake Baikal- The world's oldest, largest, and deepest freshwater lake!
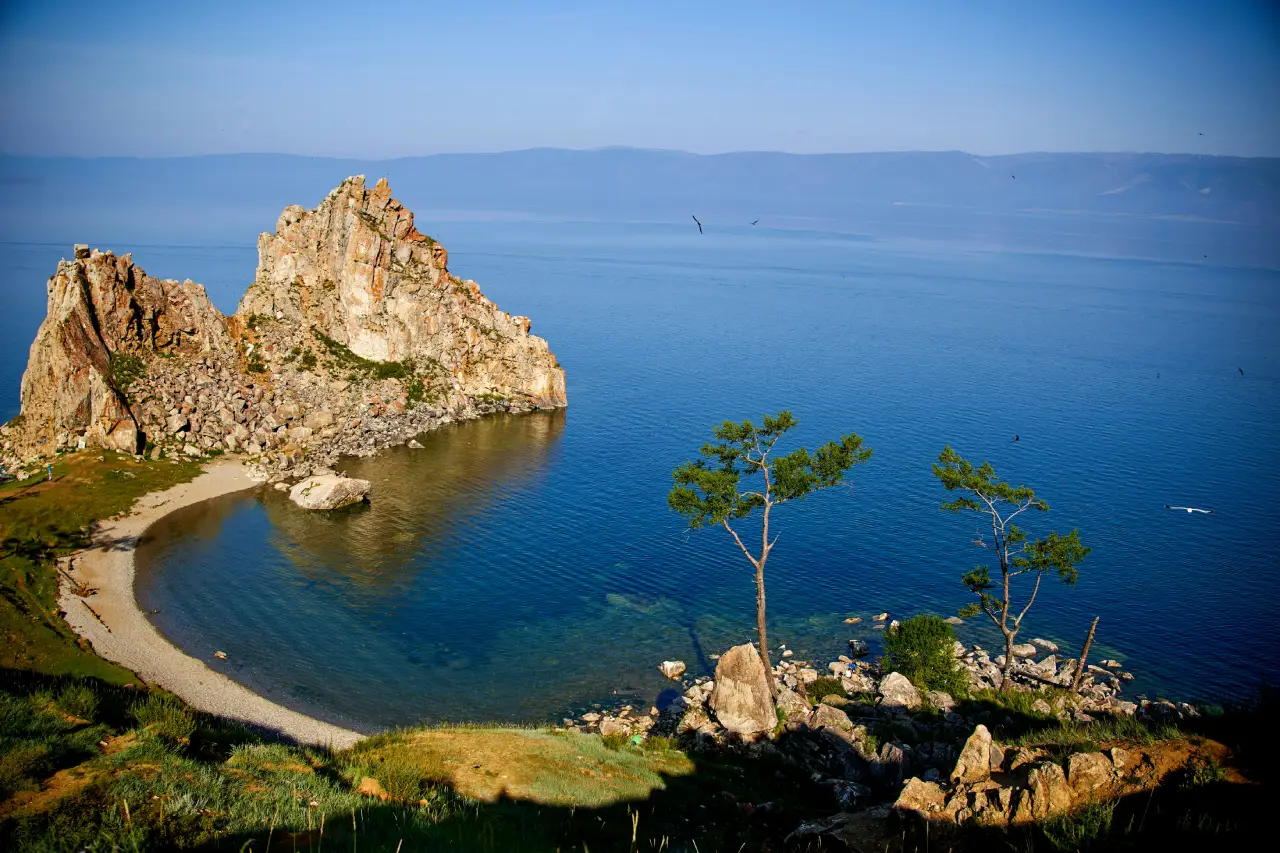

Lake Baikal is located in Siberia, a region in central Russia.
The lake is curved in shape, nearly 400 miles (645 km) long, and is more than 5,000 feet (1524 meters) deep. Most lakes formed within a bowl-shaped crater in the ground are called basins. Basins can fill with water after an ice age. This happens when glaciers melt after a volcano creates a caldera. Basins can also be formed from a river that twists or curves, circling back on itself.
Lake Baikal is unique! It was formed in a rift on the Asian tectonic plate as water filled the deep rift valley. Geologists estimate Lake Baikal formed during the Mesozoic era, somewhere between 20-25 million years ago. This is also home to the world’s only freshwater seal.