By Sakshi Kabra Malpani, Publishing Associate: Researcher and Writer at Save the Water™ | February 21, 2025
Edited by Muhammad Afridi, Publishing Associate: Project Leader at Save the Water™
Electrocoagulation is a method used in wastewater treatment. It reduces the need for chemicals and minimizes sludge production. As a result, this makes it a cleaner and more efficient process. This technique is widely used in industrial wastewater treatment. It is simple, versatile, and lowers the release of toxic byproducts.
What is Electrocoagulation?
The coagulation process in wastewater treatment uses chemicals that destabilize pollutants. This clumps them together to form larger heaps. Consequently, these heaps settle to the bottom of the water bodies and are removed by filtration and sedimentation processes.
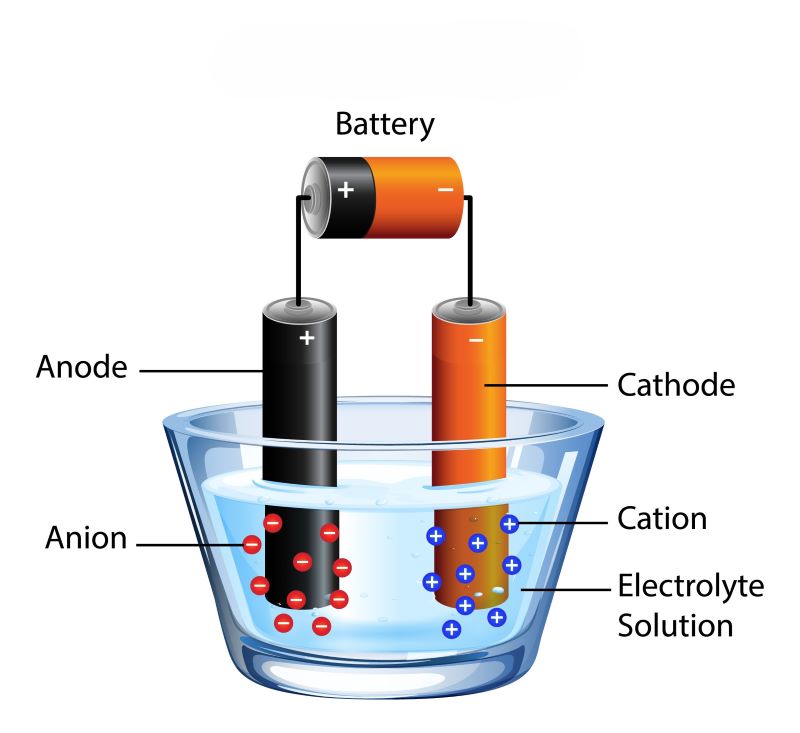
On the contrary, in electrocoagulation, chemicals are replaced by electric current. Basically, it is electrically induced coagulation. It can efficiently remove toxic chemicals, heavy metals, dirt, and suspended matter.
How Does Electrocoagulation Work?
This process uses metal electrodes—typically made of iron or aluminum—placed in wastewater. When an electric current is applied:
- The anode (positive electrode) releases metal ions.
- The cathode (negative electrode) reacts with water to form hydroxide ions.
- These metal ions combine with hydroxide ions, forming metal hydroxide flocs.
- The flocs act as coagulants, attracting and neutralizing pollutants. Thus, they settle at the bottom and are removed as sludge.
Its Use Cases in Wastewater Treatment
A group of scientists in Qatar tested electrocoagulation in treating water produced by the natural oil and gas industry. They stated that this process removes up to 99.6% of oil and gas from water. Additionally, water turbidity was reduced by 44%, and organic pollutants were significantly reduced up to 99%.
Furthermore, another study demonstrated that aluminum-based electrocoagulation can remove up to 99.76% of harmful pollutants from industrial wastewater. Thus, it can save water reservoirs from potential damage. Moreover, it can also remove more than 80% of toxic metals like nickel, chromium, iron from mine water.
In addition, this process is also effective in treating hospital wastewater and can remove turbidity, chemical oxygen demand, and water hardness. More than 95% of poisonous heavy metals like nickel, copper, lead, and zinc can be removed by this technique.
Pros and Cons
The above use cases show that electrocoagulation is a highly effective wastewater treatment technique. It does not require surplus chemicals. Thus, it is eco-friendly and generates less waste beyond the process. Moreover, it is simple to operate and requires minimal supervision and maintenance. However, despite such advantages, this technique has some disadvantages:
- Energy dependence: Relies on electricity, increasing costs.
- Electrode usage: Over time, electrodes degrade and require replacement.
- Heat generation: Can produce excess heat, making it difficult to operate.
- Scaling: Can affect long-term performance and efficiency.
Future Steps
Researchers combined other techniques with electrocoagulation to make hybrid treatment systems, to reduce its limitations. For example, these techniques can be: ozone treatment, membrane filters, adsorption, ultraviolet rays, reverse osmosis, etc.
Furthermore, scientists are working on alternative electrode materials to reduce wear and tear. This is to optimize electrocoagulation parameters to achieve more efficiency.
Researchers are trying to combine this technique with automation and renewable energy sources to cut the overall cost and large-scale implementation. Besides all this, we can also spread awareness to educate society about this technique.