By Sakshi Kabra Malpani, Publishing Associate: Researcher and Writer at Save the Water™ | June 12, 2024
Rooftop rainwater harvesting is an ancient and sustainable approach to managing water resources. Currently, it is applied to mitigate flood and drought risks. As the world combats water scarcity, this technique is a viable way to boost water supply, reduce reliance on conventional water sources, and ease the impact of urbanization. Additionally, we can use collected rainwater for both domestic and agricultural purposes, making this technique a versatile solution to modern water challenges.
What is Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting?
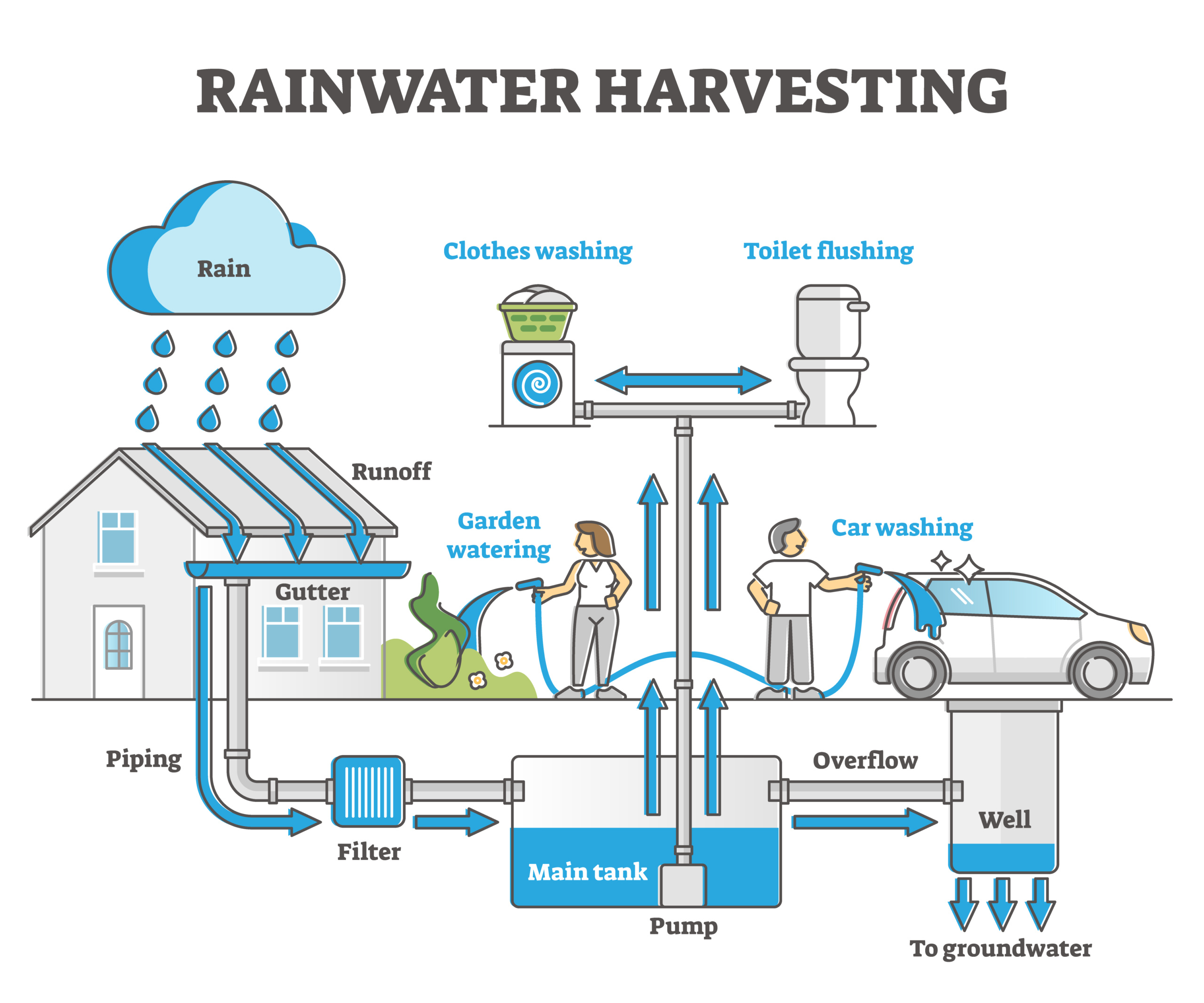
Rooftop rainwater harvesting involves using gutters to collect the rainwater falling on roof surfaces and storing it in reservoirs. According to the United Nations Agenda 2030, over 2 billion people are living in areas experiencing critical water stress. Thus, rooftop rainwater harvesting reduces the dependence on conventional water sources and helps conserve groundwater and surface water resources.
Households commonly collect rainwater in cisterns, tanks, and barrels in open spaces. Public areas usually collect rooftop rainwater in stepwells, water cellars, and qanats through pipelines. The Desert Research Institute and the University of Nevada have successfully used this technique to cultivate food crops in their community garden.
Basics of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
The basic components of rooftop rainwater harvesting include collection, transportation, storage, and distribution systems:
- The collection system consists of a catchment area or rooftop surface from where rainwater will be collected. Rooftops often built with cement tiles or galvanized or corrugated metal sheets are best for harvesting superior-quality rainwater.
- The transportation system comprises channels, downpipes, or gutters that direct the collected rainwater from the rooftop to the storage system. They should be made up of durable plastic or galvanized metals. Nowadays, these systems are fitted with filters. The filters remove dirt, twigs, pebbles, and small leaves that can pass through the gutters along with captured rainwater. Additionally, it may contains a first flush diverter, which diverts the initial flow of water away from the storage system. This is because the first flush of rain generally contains most of the contaminants on the rooftop.
- The storage system is simply the water reservoir. These reservoirs could either be underground like tanks, wells, or cisterns, or above the ground such as barrels, rain gardens, or ponds. The size, material, and location of reservoirs depend on the amount and potential use of the collected rainwater. Further treatment with sand, gravel, sponge, and charcoal filters can make the collected water suitable for drinking purposes. For irrigation, additional filtration is usually not required.
- The distribution system is made up of pumps and pipes that convey the collected rainwater to the points of use.
Benefits of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
- Firstly, it helps in water conservation and lowers rainwater runoff.
- This is a self-sufficient, simple, cost- and energy-saving technique.
- Moreover, it ensures the protection of water resources and diminishes the demand for surface water and groundwater.
- Its operational cost is low and maintenance is easy.
- You can build this kind of system anywhere, irrespective of the area’s geology, geography, climate conditions, and infrastructure.
- Additionally, people can filter the water collected using this technique for potable purposes.
- Lastly, it helps in flood control, stormwater management, and protection of soil from erosion.
Challenges of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
Despite the benefits listed above, this technique is not without some challenges. For example, there are potential health risks of illness and infection associated with the drinking quality of stored rainwater.
Organizations doing manual surveys to determine the availability of rooftop areas for rainwater harvesting also experience difficulties. These include limited access to rooftops, measurement errors, and many more. Furthermore, the gutters and pipes used for rooftop rainwater harvesting may clog after prolonged use.
There are some simple measures that can be taken to ease these challenges:
- Regular cleaning of the gutters, pipes, and filters.
- Periodic inspection of all component systems to ensure their proper functioning.
- Regular testing of the quality of water harvested using this technique.
- Design of systems according to the specific water demand.
Looking Ahead
Beyond manual surveys, advanced remote sensing technology and satellite images are now used for site analysis. However, satellite images sometimes fail to give the accurate views of the rooftops, especially for small apartments. Thus, scientists are now developing unmanned aerial vehicles to provide high-resolution spatial images of rooftops at all scales and levels.